HEAD STYLES
The screw head houses the drive system and transmits clamping force to the parts to be assembled. The head design will depend on its function in the application, the bearing surface must be large enough so that the clamping force does not deform the cover part.
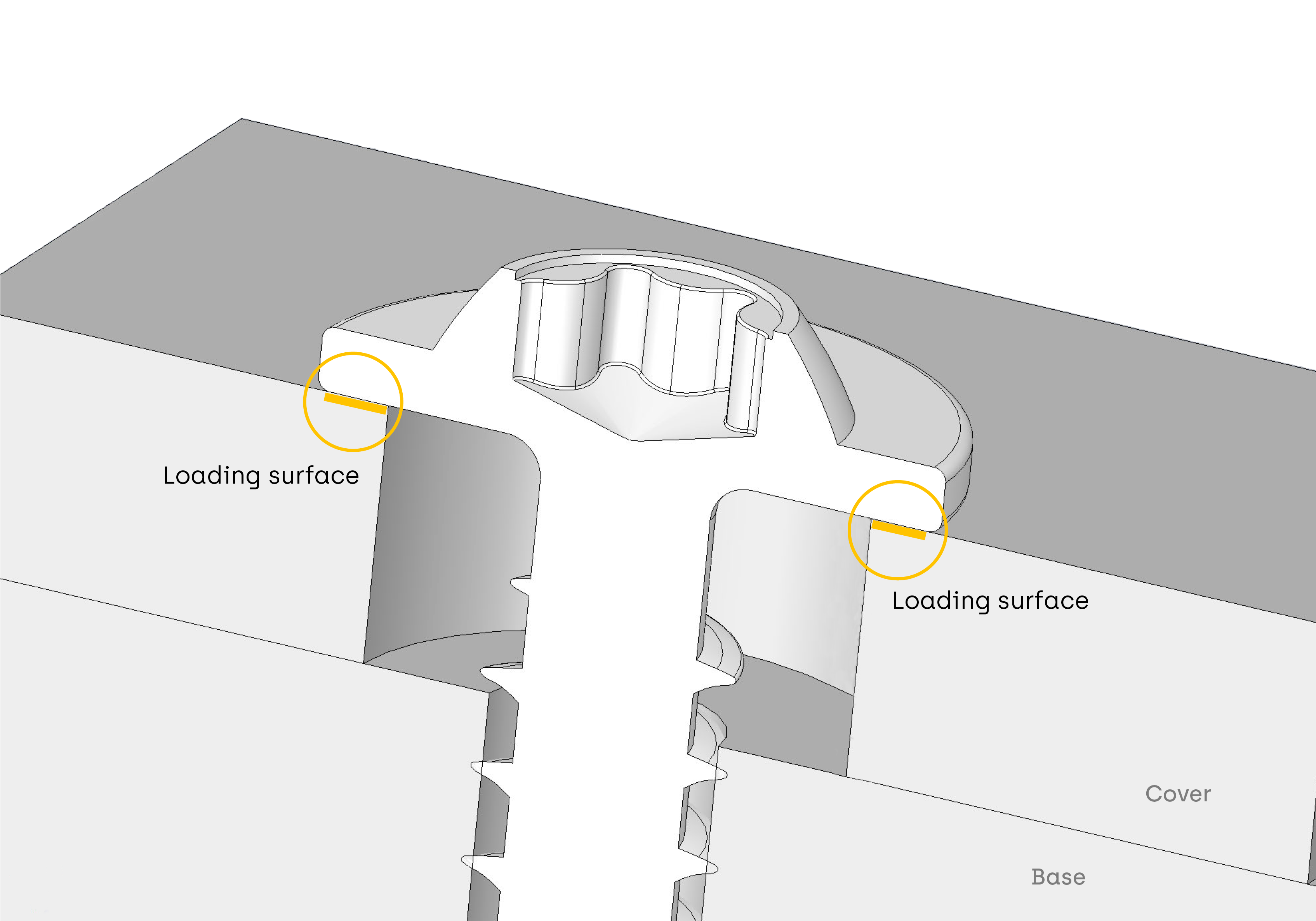
Whenever possible, it is recommended to follow ISO/DIN standards for each type of screw. ISO/DIN standards specify the head dimensions for different driving systems, thread type and strength category. These general recommendations can be modified in accordance with the application requirements, reducing or increasing head height or diameter, or adding a flange. Our Application Engineers use special software to find out the optimal design of the screw head to best fit for your application requirements and installation.
Have a question about screw heads or complex screw head designs?
The size of the screw head depends on the mechanical requirements and cover material. Many applications require a high head-to-shank ratio, that’s an oversized screw head compared to the thread diameter. In these cases, it is important to analyze the feasibility of the heading process and proceed to manufacture in a multi-station cold forming process or second operations in CNC machining.
Some examples are:
- Screws with a larger washer for applications that require a higher surface contact
- Screws with bigger heads to avoid breaking during assembly
- Over-molding screws or ball studs
- Other functional screws
Head geometries
Depending on the application requirements, head styles can be featured with different drive systems (POZI, PHILLIPS, TORX PLUS®, AUTOSERT®...).
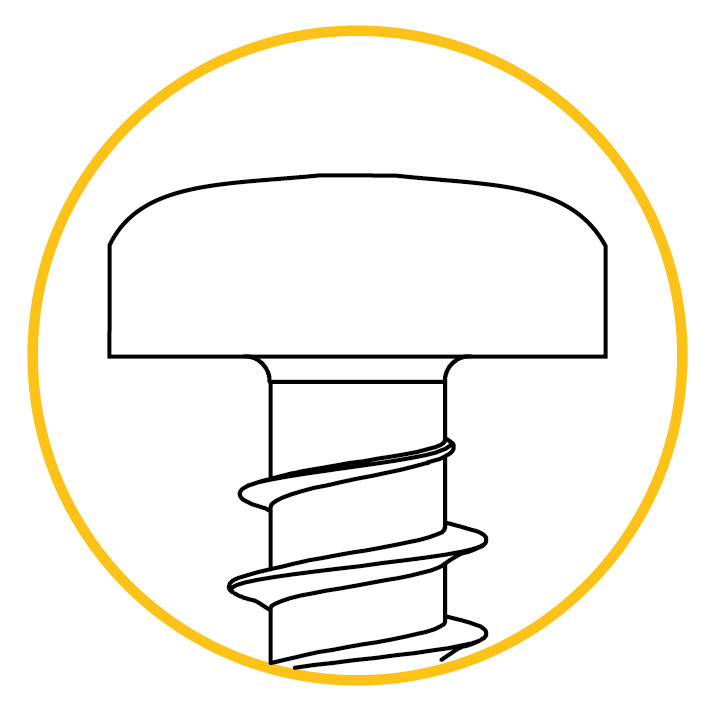
Pan head
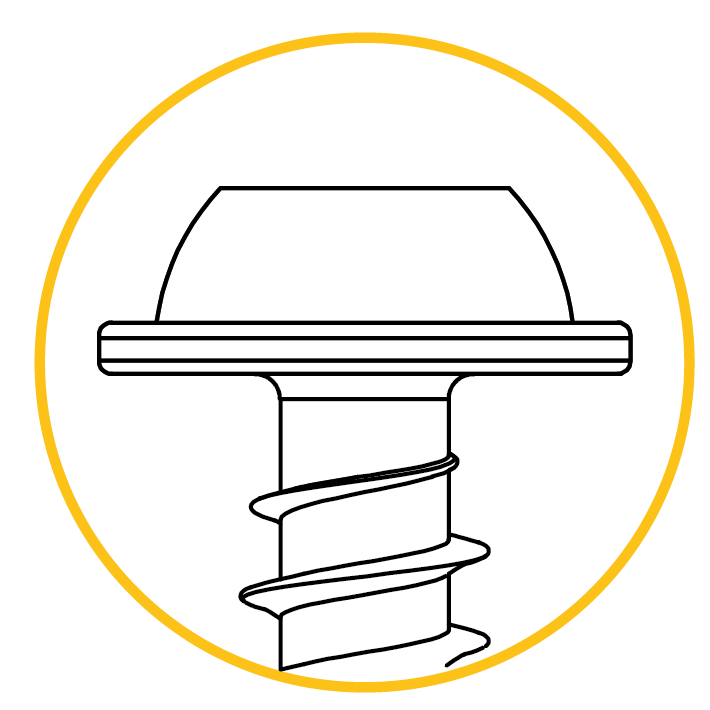
Pan head flange
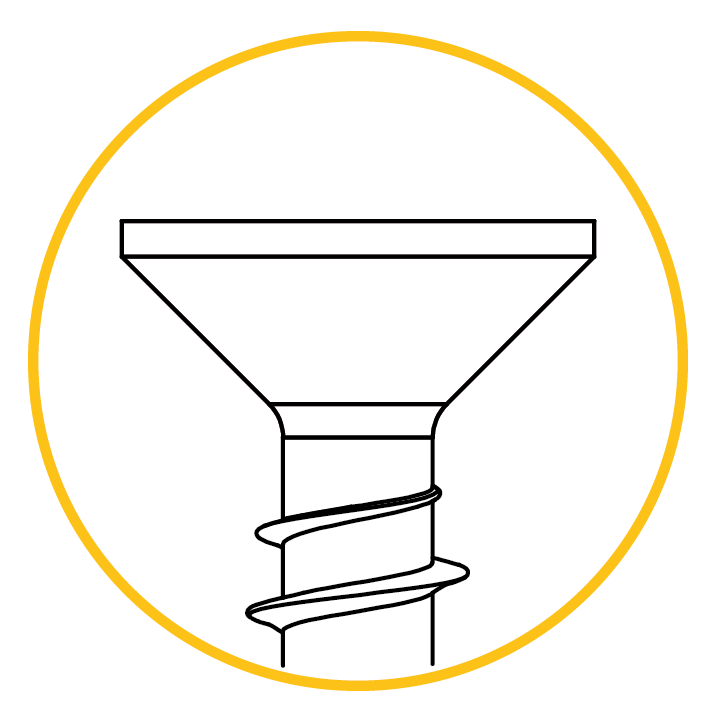
Countersunk head
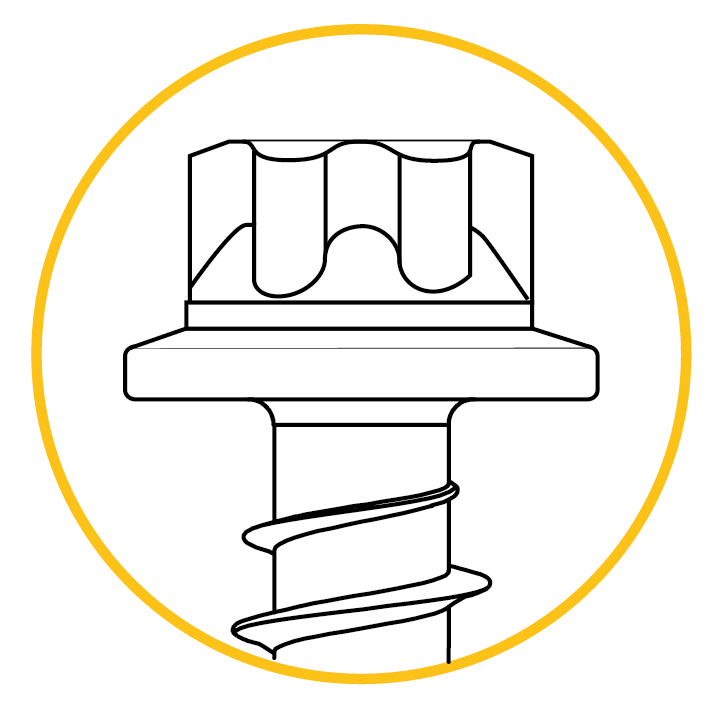
TORX PLUS® External
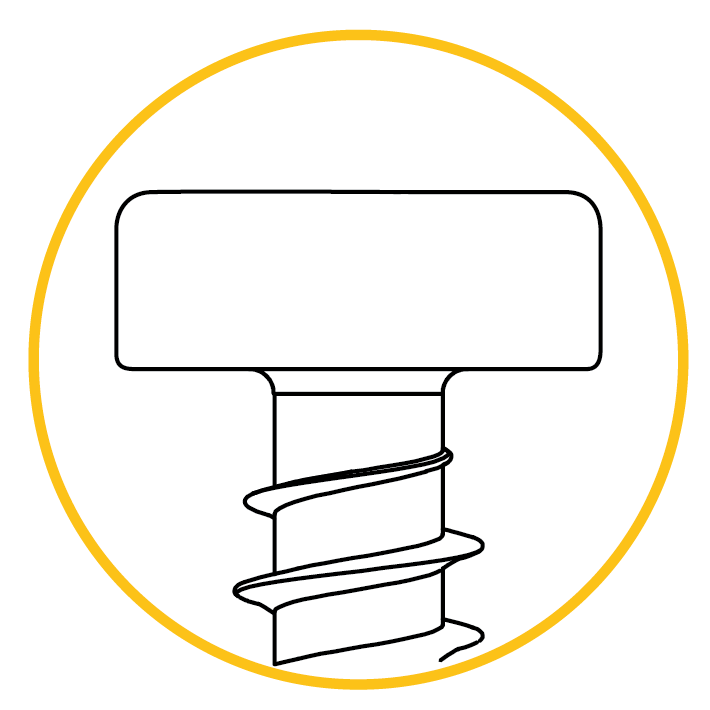
Cylindrical head
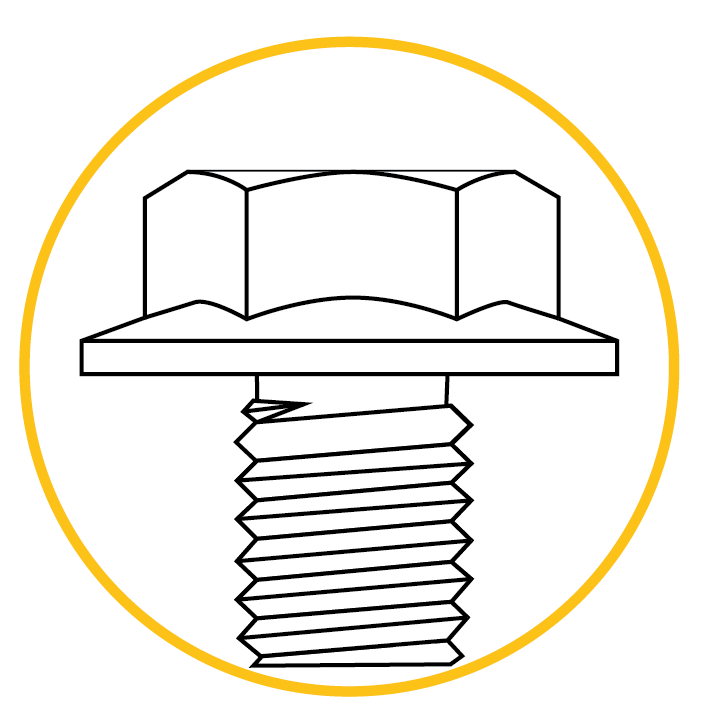
Hexagonal flange
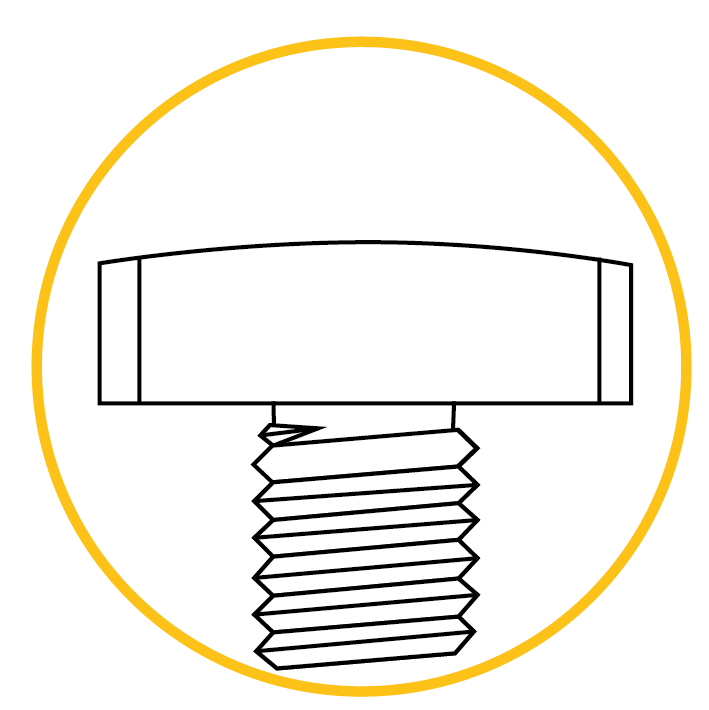
Square head
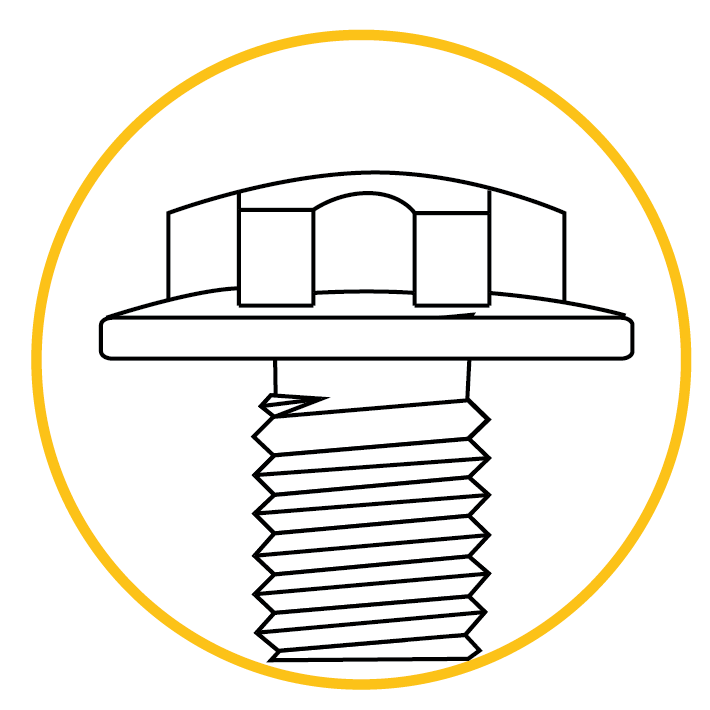
TORX PLUS® Low Profile
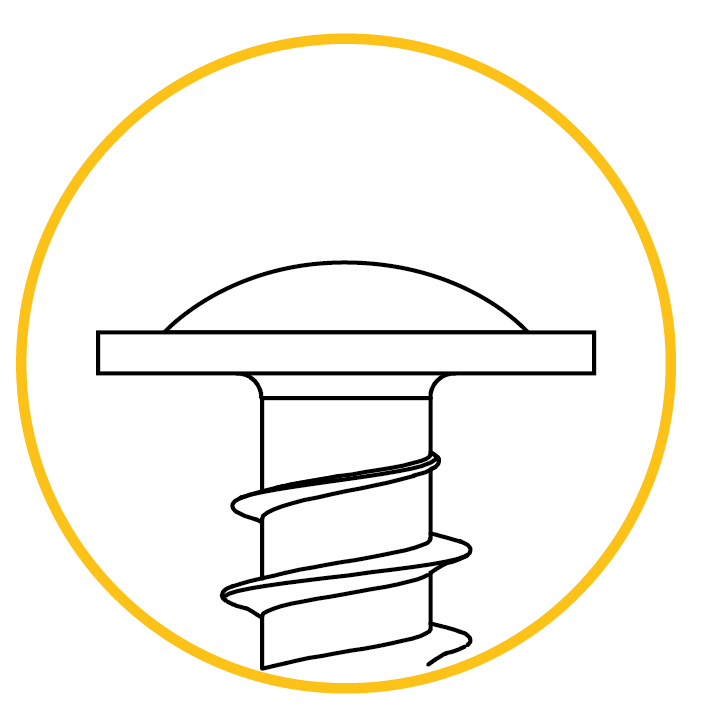
Extra low head
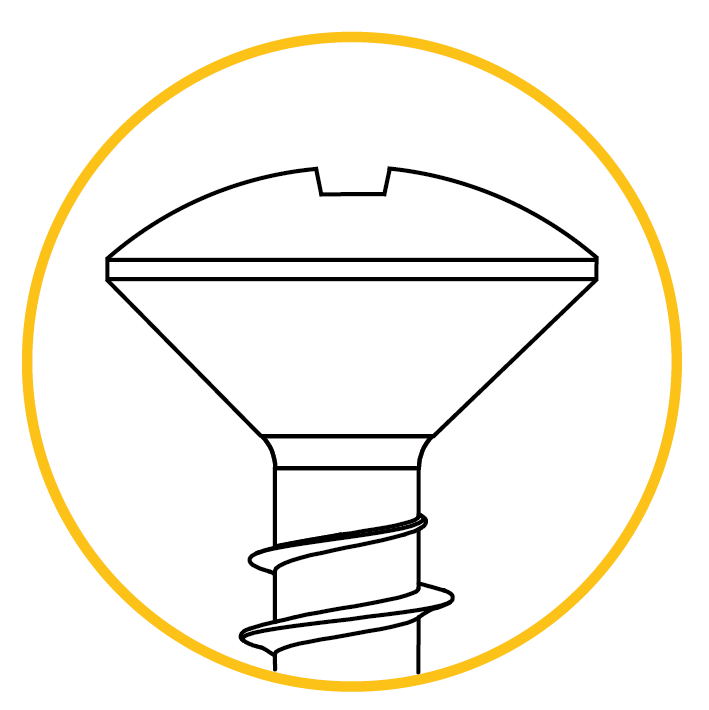
Oval Countersunk